XWater-Soluble: absorbed with water and enter the bloodstream directly
XFat-Soluble: need dietary fat to be absorbed properly; pass through small intestine and into lymphatic system before entering the bloodstream (Vitamin A , K and E are stored in liver; Vitamin D is stored in fat and muscle tissue)
Vitamin A (Retinol)
XBenefits: prevents eye problems, necessary for wound healing and normal immune function, helps keep skin healthy, essential for growth and development of cells
XSources: milk, eggs, liver, fortified cereals, darkly colored orange or green vegetables (carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, kale) and orange fruits (cantaloupe, apricots, peaches, papayes and mangos)
XDeficiency: Night blindness, dry eyes, poor bone grwoth
XToxicity: Fatigue, Night Sweats, Vertigo, Headache, Bne Pain, Vomiting, Jaundice, Hypercalcemia
Vitamin D (Cholecalciferol)
XBenefits: necessary for bone formation; promotes absorption of calcium and phosphorous
XSources: egg yolk, liver, fatty fish, sunlight
XDeficiency: Rickets
XToxicity: Hypercalcemia, Vomiting, Retarded Growth
Vitamin E (Tocopherol)
XBenefits: anti-oxidant and helps protect cells from damage; important for health of red blood cells
XSources: vegetable oils; liver; egg yolk; butter; green leafy vegetables; whole-grain breads; cereals
XDeficiency: Hemolytic anemia; Hyporeflexia; Spinocerebellar and Retinal degeneration
XToxicity: May interfere with vitamin K which leads to prolonger clotting and bleeding time
Vitamin K (Phylloquinone)
XBenefits: needed for normal blood clotting
XSources: green leady vegetables, soy beans, vegetable oild
XDeficiency: Bleeding due to deficiency of prothrombin and other factors (clotting); Osteopenia
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin)
XBenefits: helps the body convert carbs into energy and is necessary for the heart, muscles, and nervous system to function properly
XSources: whole grains; meat; enriched cereals, nuts, legumes, potatoes
XDeficiency: Wernicke encephalopathy; Korsakoff syndrome; Beriberi
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
XBenefits: releases energy from protein, fat and carbohydrates; promotes healthy skin and eyes
XSources: milk, cheese, liver, meat, eggs, enriched cereals
XDeficiency: Cheilosis, Normochromic-Normocytic Anemia
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
XBenefits: releases energy from protein, fat and carbohydrates; helps maintain healthy skin and is important for nerve function; involved in cholesterol production; guards against birth defects
XSources: liver, red meat, fish, poultry, legumes, whole-grain or enriched cereals
XDeficiency: Pellagra
XToxicity: Flushing
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acids)
XBenefits: releases energy from protein, fat and carbohydrates
XSources: corn, cauliflower, kale, broccoli, tomatoes, avocados, liver, leat, egg yolk, yeast, whole-grain breads, cereals, legumes, vegetables
XDeficiency: Fatigue, Sleep disturbances; Nausea; Muscle Cramps
XToxicity: Diarrhea; water retention
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
XBenefits: important for normal brain and nerve function; helps the body break down proteins and make red blood cells
XSources: Organ meats, whole-grain cereals, fish, legumes
XDeficiency: Seizures, anemia, neuropathies
XToxicity: Peripheral Neuropathy
Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
XBenefits: essential component of enzymes
XSources: Peanuts, Tomatoes, Almonds, Eggs, Onions, Carrots, Romaine Lettuce, Cauliflower, Sweet Potato, Oats
XDeficiency: Hair loss; Rash around eyes, noise, mouth and genital area; Depression, Lethargy, hallucination, and numbness of the extremities
Vitamin B9 (Folate; Folic Acid)
XBenefits: helps prevent birth defects; important for a healthy heart and cell development
XSources: dark, leafy vegetables; enriched and whole grain breads; fortified cereals
XDeficiency: Megaloblastic Anemia; Macrocytic Anemia
Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin)
XBenefits: helps to make red blood cells, nerve cells and DNA; helps break down carbs and fat
XSources: meats, poultry, eggs, fortified cereals, milk and milk products
XDeficiency: Pernicious Anemia
X**important for vegans to supplement because B12 is only found in animal products
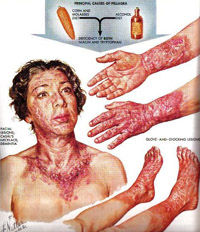
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
XBenefits: forms collagen (essential for skin, blood vessels, bones and teeth); acts as an antioxidant; provides resistance to infections and promotes wound-healing
XSources: citrus fruits, tomatoes, potatoes, broccoli, strawberries, sweet peppers
XDeficiency: Scurvy
 D. Kyle.
Red Raider at TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY Ŧ. Avid Tweeter. Omnivore. 10 fingers and 10 toes. Known for
D. Kyle.
Red Raider at TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY Ŧ. Avid Tweeter. Omnivore. 10 fingers and 10 toes. Known for